개요
현재 로직에는 잠재적인 문제가 존재한다
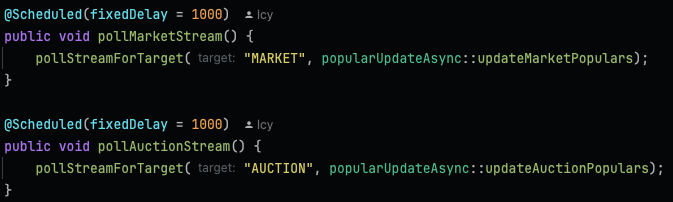
비동기 방식으로 캐시 갱신 쿼리를 실행할 경우, 최소 1초에 한 번 실행될 수 있다.
하지만 일시적인 DB 부하로 인해 쿼리 실행 시간이 1초 이상 걸리는 상황이 발생한다면, 다음과 같은 문제가 생길 수 있다
1. 동일 작업이 중복 실행되어 jvm의 스레드 자원이 낭비된다.
2. 캐시 갱신 타이밍이 겹치면서 race condition이 발생할 수 있다.
3. 불필요한 느린 쿼리들이 중복 호출될 수 있다(현재 기준 동일 네트워크 상에서 평균 600ms로 빠른 편이 아니다)
-> 결과적으로 어플리케이션, DB, Redis 모두에 영향을 끼칠 수 있다.
Semaphore
세마포어를 활용해 비동기 메서드 실행을 하나의 스레드로 제한하는 방식으로 문제를 해결할 수 있다고 판단했다.
세마포어란 임계영역에 동시에 접근할 수 있는 스레드 수를 제한하는 동기화 도구로,
java에선 tryAcquire()로 락 점유 여부를 비차단 방식으로 확인할 수 있고, 성공한 스레드만 임계 영역으로 보내며 나머지 스레드는 즉시 반환하도록 구현할 수 있다.
이 구조는 jvm단에서 실행 흐름을 제어하기 때문에, db나 redis에 접근하기 전 애초에 불필요한 연산을 차단할 수 있어서 시스템 리소스 보호에 효과적일 것이다.
또한 세마포어에 걸려 return 된 비동기 작업은 실제로 실행되는 로직도 없고 외부에서 참조되지 않는다면 gc가 바로 수거하므로, 어플리케이션 전체에 주는 부담도 거의 없을 것이다.
테스트코드로 검증
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class PopularUpdateAsync {
private static final String MARKET_CACHE_KEY = "popular:market:items";
private static final int POPULAR_LIMIT = 200;
private final Semaphore marketSemaphore = new Semaphore(1);
private final AtomicInteger executionCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Async
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void updateMarketPopulars() {
if (!marketSemaphore.tryAcquire()) {
return;
}
try {
executionCounter.incrementAndGet();
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0, POPULAR_LIMIT);
Page<MarketPopularResponseDto> result = marketRepository.findPopularMarketItems(getStartDate(), pageable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
MARKET_CACHE_KEY,
serialize(result.getContent())
);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
marketSemaphore.release();
}
}
public int getExecutionCount() {
return executionCounter.get();
}
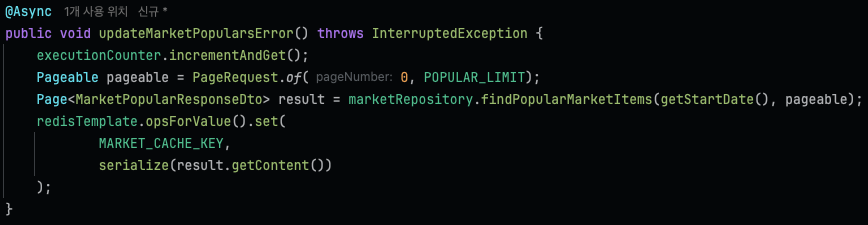
@Async
public void updateMarketPopularsError() throws InterruptedException {
executionCounter.incrementAndGet();
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0, POPULAR_LIMIT);
Page<MarketPopularResponseDto> result = marketRepository.findPopularMarketItems(getStartDate(), pageable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
MARKET_CACHE_KEY,
serialize(result.getContent())
);
}
}Thread.sleep(1000) 으로 db에 병목이 걸린 상황을 가정하였다.
Semaphore(1)로 접근할 수 있는 스레드 수를 1개로 차단한다.
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class PopularUpdateAsyncConcurrencyTest {
@Autowired
private PopularUpdateAsync popularUpdateAsync;
@Test
void 인기_마켓_동시_갱신_실행_테스트_락_없이() throws InterruptedException {
int threadCount = 5;
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
log.info("=== 테스트 시작 ===");
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
executorService.submit(() -> {
try {
log.info("스레드 {}: 호출 시작", Thread.currentThread().getName());
popularUpdateAsync.updateMarketPopularsError();
log.info("스레드 {}: 호출 완료", Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
int executions = popularUpdateAsync.getExecutionCount();
log.info(">>> 실행된 쿼리 횟수 = " + executions);
Assertions.assertEquals(5, executions, "이게왜안됨!");
}
@Test
void 인기_마켓_동시_갱신_실행_테스트_세마포어() throws InterruptedException {
int threadCount = 5;
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
executorService.submit(() -> {
try {
log.info("스레드 {}: 호출 시작", Thread.currentThread().getName());
popularUpdateAsync.updateMarketPopulars();
log.info("스레드 {}: 호출 완료", Thread.currentThread().getName());
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
int executions = popularUpdateAsync.getExecutionCount();
log.info(">>> 실행된 쿼리 횟수 = " + executions);
Assertions.assertEquals(1, executions, "이게왜안됨!");
}
}동시에 5개(사실 쿼리 병목이 1초라면 동시에 2개만 실행되겠지만 테스트코드니까)의 스레드를 보내어 테스트해보면,
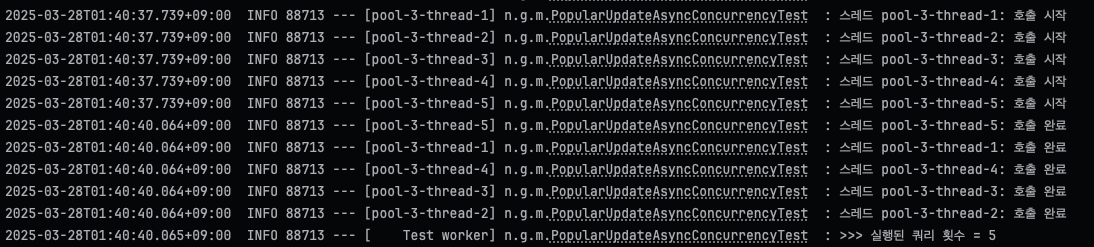
세마포어 적용 전에는 모든 비동기 스레드가 동시에 실행되어 1초 후 일괄 완료되었지만,
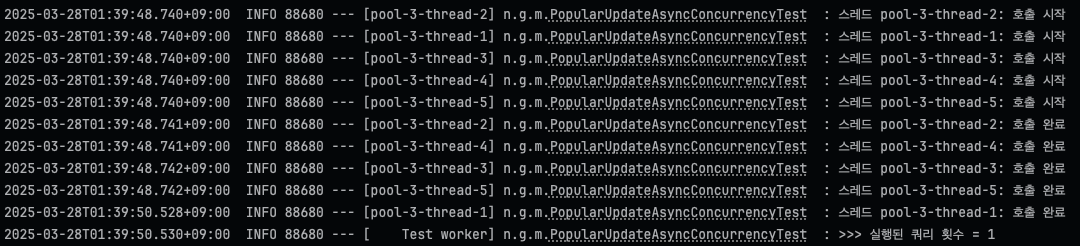
적용 후에는 단 하나의 스레드만 1초짜리 작업을 수행하며 나머지는 실행되지 않았다.
회고
비동기적으로 실행되는 작업의 중복 실행을 방지해서, 어플리케이션의 잠재적인 위험을 줄일 수 있었다.
비동기 실행과 동시성 제어가 상호 보완적으로 작동하는 구조를 직접 구현해보니 재밌고 뿌듯하다
운영체제 이거 공부해서 어디다가 써먹지? 생각했는데, 역시 아는 만큼 보인다는 말이 맞는 거 같다. 세마포어를 몰랐다면 내가 어떻게 처리했을까?
책 열심히 읽어야겠다..
'팀 프로젝트 > market.normalization.project' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Actuator가 자동으로 Session을 생성한다 (0) | 2025.04.02 |
|---|---|
| 조회 성능 향상시키기(4) 인기 품목 조회 최적화 (0) | 2025.03.24 |
| 조회 성능 향상시키기(3) Pagination Count Query 최적화 (0) | 2025.03.23 |




